Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Crystal Field Splitting Theory, Crystal Field Splitting in Tetrahedral Complexes, Strong Field Ligands & Weak Field Ligands etc.
Important Questions on Crystal Field Theory
: [Ti(H2O)6]4+ is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless.
: d - d transition is not possible in [Sc(H2O)6]3+
The correct order for the wavelengths of absorption in the visible region for the following is:
The value of the spin only magnetic moment for one of the following configurations is BM. The correct one is
Define weak field ligands.
Define strong field ligands.
The crystal field theory does not consider the _____ character in metal-ligand bonding.
Write any two limitation of crystal field theory.
Which of the following compounds is not coloured?
An octahedral complex with magnetic moment may have:
(a) configuration with weak field ligand.
(b) configuration with strong field ligand.
(c) configuration with strong field ligand.
(d) configuration with weak field ligand.
Crystal field splitting energies for octahedral and tetrahedral geometries caused by the same ligands are related through the expression
The order of octahedral crystal field energy for orbitals are
According to crystal field theory, total number of unpaired electrons present in the following molecules and will be
For next two question please follow the same
When degenerate -orbitals of an isolated atom/ion come under influence of magnetic field of ligands, the degeneracy is lost. The two set t2g (dxy, dyz,dxz) and eg (dz2, dx2-y2) are either stabilized or destabilized depending upon the nature of magnetic field. It can be expressed diagrammatically as :
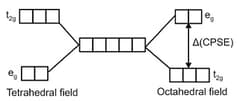
Value of depends upon nature of ligand and a spectrochemical series has been made experimentally, for tetrahedral complexes, is about times to ( for octahedral complex). This energy lies in visible region and i.e., why electronic transition are responsible for colour. Such transitions are not possible with and configuration.
form four complexes with four different ligands which are [Cr(Cl)6]3-, [Cr(H2O)6]3+, [Cr(NH3)6]3+ and [Cr(CN)6]3-. The order of in these complexes is in the order :
Explain in detail the limitation of Crystal Field theory.
State any two limitations of Crystal Field Theory.
Increasing crystal field strength of the different ligands is :
Blue coloured copper sulphate solution gave following experimental results. Explain the same. With aqueous potassium fluoride it gave a green precipitate.
Blue coloured copper sulphate solution gave following experimental results. Explain the same. With aqueous potassium chloride it gave bright green solution.
What are weak field and strong field ligands? What is spectrochemical series?
In an octahedral crystal field, draw the figure to show splitting of -orbitals.
